Comtarsia SignOn Agent for Active Directory 7.0
Table of Contents
Version: 7.0.4.1, July 11, 2025
Introduction
Automated Active Directory Account Management triggered by Logon Client, Web Gateway and LDAP Directory Replicator via the SignOn Proxy Service.

Supported Platforms:
Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022 /2025 Domain Controllers or remote access to Domain Controllers
Installation
1. Manual Installation
An installation or an update is done using the installation program “SOS2012-6.0.x.4.exe”. When updating, the configuration is preserved and the license key will only be replaced if the validity of the installed key is shorter than the validity of the key shipped with the installation program. (Bought license keys usually won’t be replaced.)
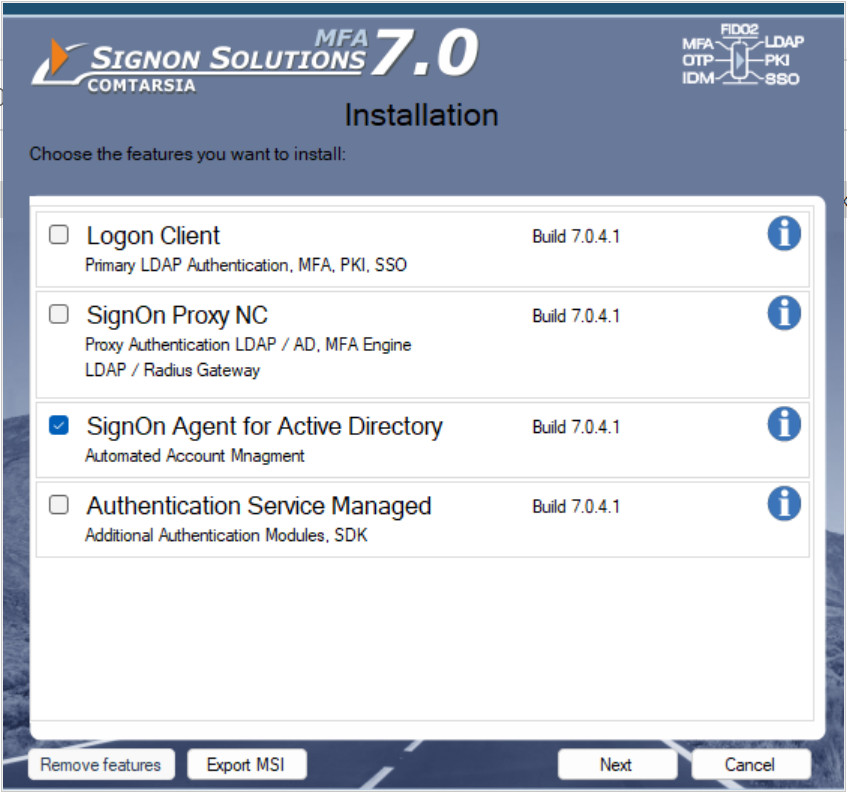
After the installation, the configuration utility „Comtarsia Management Console“ is started. See: Comtarsia Management Console (ComtMC)
Configuration
The SignOn Agent for Active Directory is configured through the Comtarsia Web Management. A shortcut to the Web Management can be found in the start menu.
You are first presented with a login dialog like below:
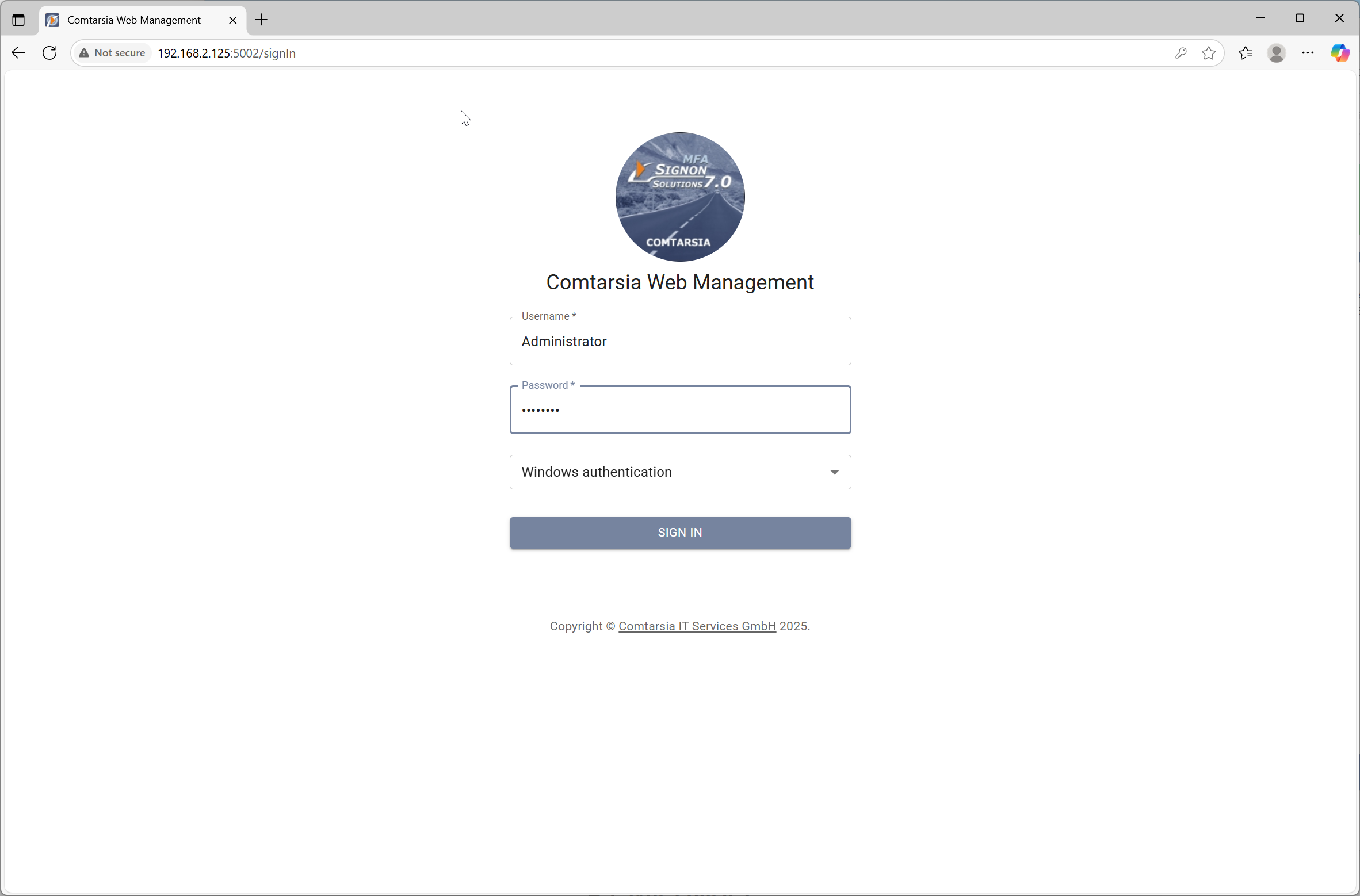
Enter the credentials of an administrative user and press Sign In.
2. Dashboard
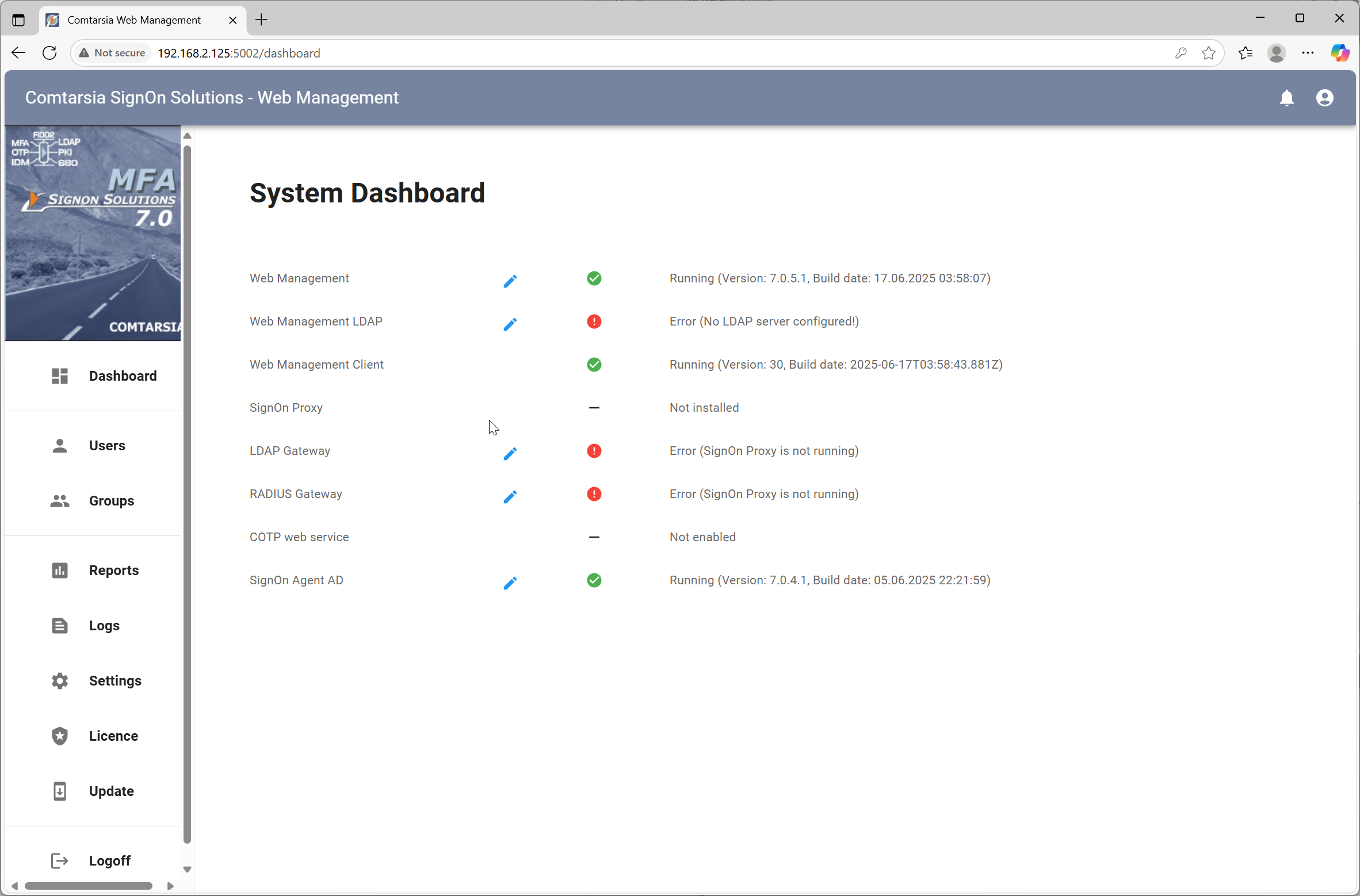
After login, you are first presented with the dashboard.
There you can see the status of all installed SignOn Solution services. On the top right of the page you have a notification bell, which will notify you of important events, like critical service errors or available software updates.
3. General Settings
In the menu on the left side, click Settings to change to the configuration page.
There you can see the profile of all available product to configure.
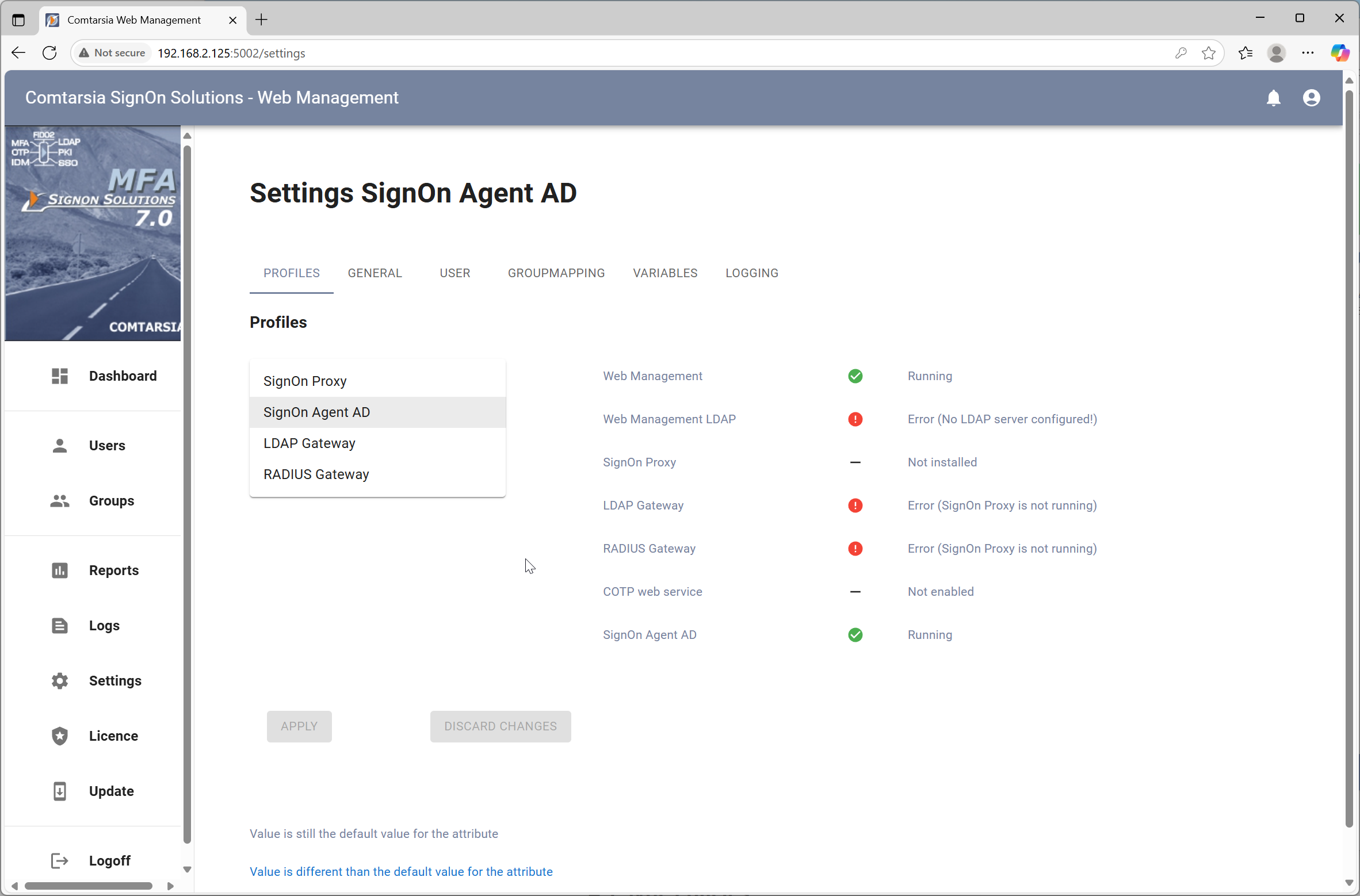
In the profiles list select SignOn Agent AD. Then with the tabs you can switch between the different configuration sections.
General covers settings like TLS certificates, allowed peer, and general Active directory settings like the default user or group containers.
The Listener interface defines the permitted SignOn Proxy request interface.
The Accept List defines SSL verification options for the communication between the SignOn Proxy and the SignOn Agent.
TLS defines the transport layer security certificates for the SignOn Gate communicate (SignOn Proxy-Logon Client; SignOn Proxy-SignOn Agent).
4. Sync Policies
In the user tab you can define the sync policy.
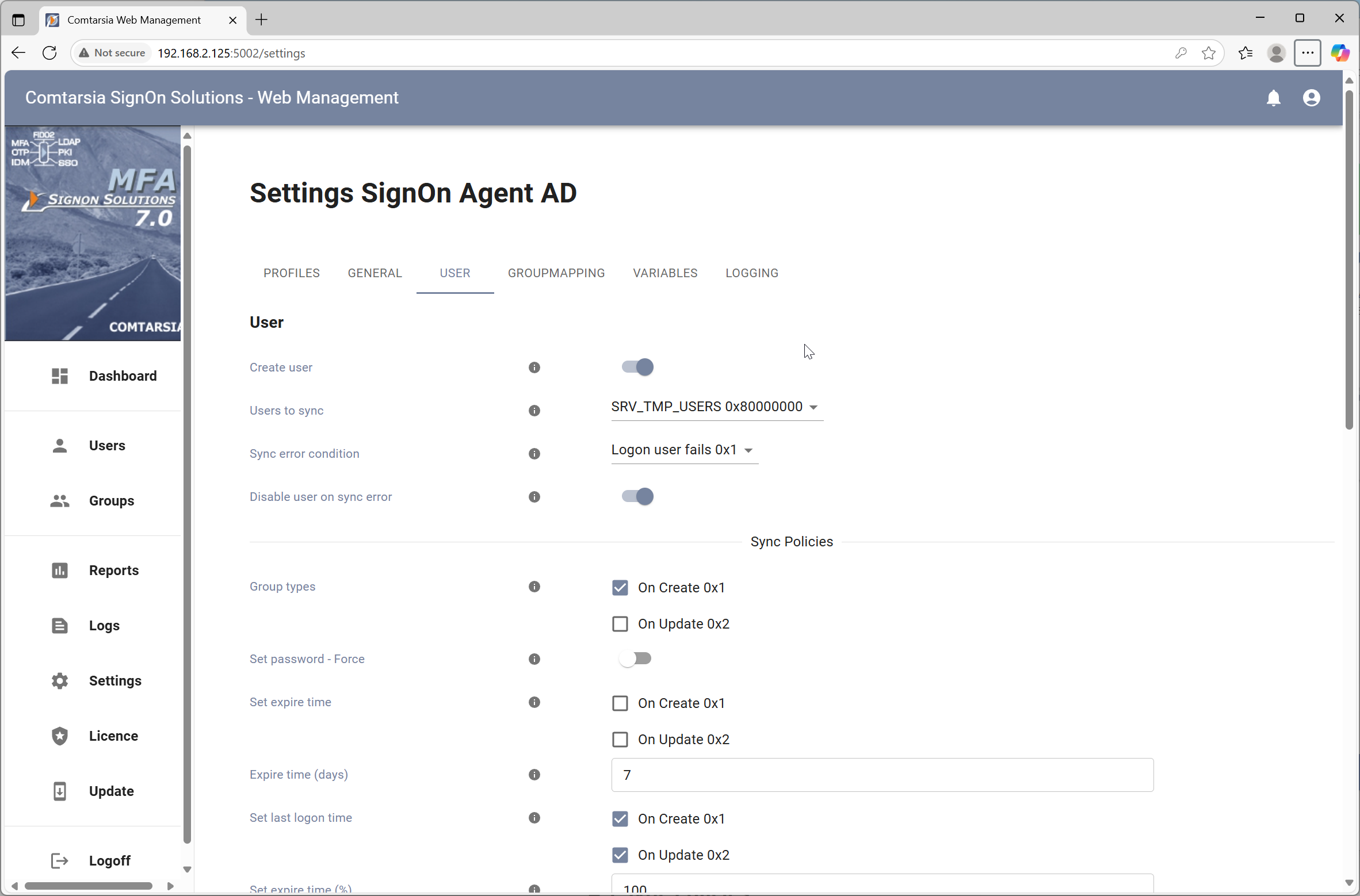
Create User defines if a user should be created or only existing users should be updated.
Active Directory user accounts created or updated by the Signon Agent gets a synchronization time stamp starting with "SERV_TEMP_USER".
The user to sync setting defines if all users or only users with the description "SERV_TMP_USER" should be updated. The setting SERV_TEMP_USERs results that only automatic created users by the SignOn Agent are managed by the Agent. With the setting "All users" the description of any user account is overwritten on each synchronization request.
The Sync error condition defines when a sync error is stated and reported back to the client. LogonUser fails: only treats a failed logon after setting this user's password as a sync error. ALL errors: treats all errors as sync error. i.e.: The Agent wasn't able to update the users's group membership.
If Disable user on sync error is enabled, the user will be disabled if a sync error is met the sync error condition setting.
set password
- OnCreate: The password is set when the user is created.
- OnUpdate: The password is updated only if the logon fails with the requested password.
- Force: The password is set on each signon request. This setting is not recommended by default, because it costs a little more performance, but it can be necessary under certain circumstances.
set expire time
- OnCreate / OnUpdate; the Active Directory user account expiration time is set.
- expire time (days): Specifies in how many days users should expire. This time is set in the AD user object.
- set expire time (%): Specifies how much time of "expire time" has to be left so that "expire time" will be set again.
- 100% = always.
- 50% = if half, or less then half of expire time is left for the user to expire, the expire time will be set again. This option can be set to less then 100% to reduce Active Directory replications on extensive Active Directory environments.
set last logon-time OnCreate / OnUpdate; the Active Direcory user account last logon time is set.
add to group OnCreate / OnUpdate; defines if a user should be added to a Active Directory group according to the group-mapping function.
remove from group OnCreate / OnUpdate; defines if a user should be removed from a Active Directory group according to the group-mapping function.
create homedir OnCreate / OnUpdate; specifies the path to the home directory to create. This value can contain variables. Example: C:\home%USERNAME% or \server1\homedirectories%USERNAME%
check homedir ACL OnCreate / OnUpdate; the ACL of the logging on user is applied to the users home directory folder. The required inheritable file permission and share rights must be applied to the parent folder manually.
create profile OnCreate / OnUpdate; Specifies the path to the user profile to create. This value can contain variables. Example: C:\profiles%USERNAME% or \server1\homedirectories%USERNAME% The required inheritable file permission and share rights must be applied to the parent folder manually. The ACL of the logging on user is applied by the windows client itself.
5. Security Agent
The settings for the Security Agent can be found on the General tab.
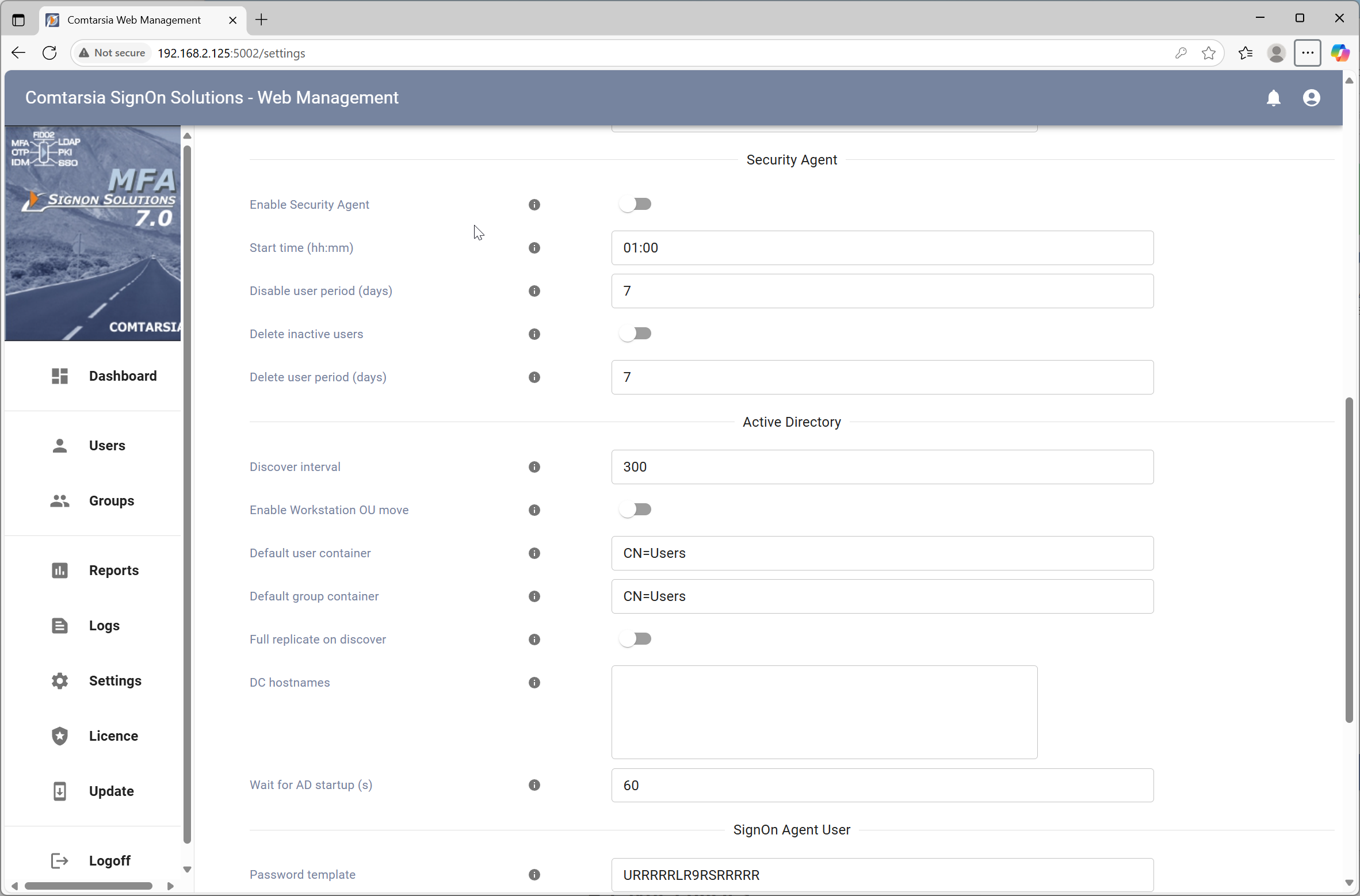
Active Directory user accounts created or updated by the Signon Agent gets a synchronization time stamp starting with "SERV_TEMP_USER".
To disable or/and delete inactive user accounts the Security Agent setting can be used.
start time (hh:mm): Specifies at which time of the day the Security Agent should process.
disable user period (days): Specifies after how many days of inactivity a user should be disabled.
delete user period (days): Specifies after how many days of inactivity a user should be deleted. It must be considered that deleted user accounts automatically recreated with a new SID by the SignOn Agent the next time the user is logs on. To avoid access problems by wrong folder or file ACL's by the home directory the delete user period should be defined rather longer and the user expiration and the disable user function should be used instead within the ordinary managed period of a user accounts.
6. Group-mapping
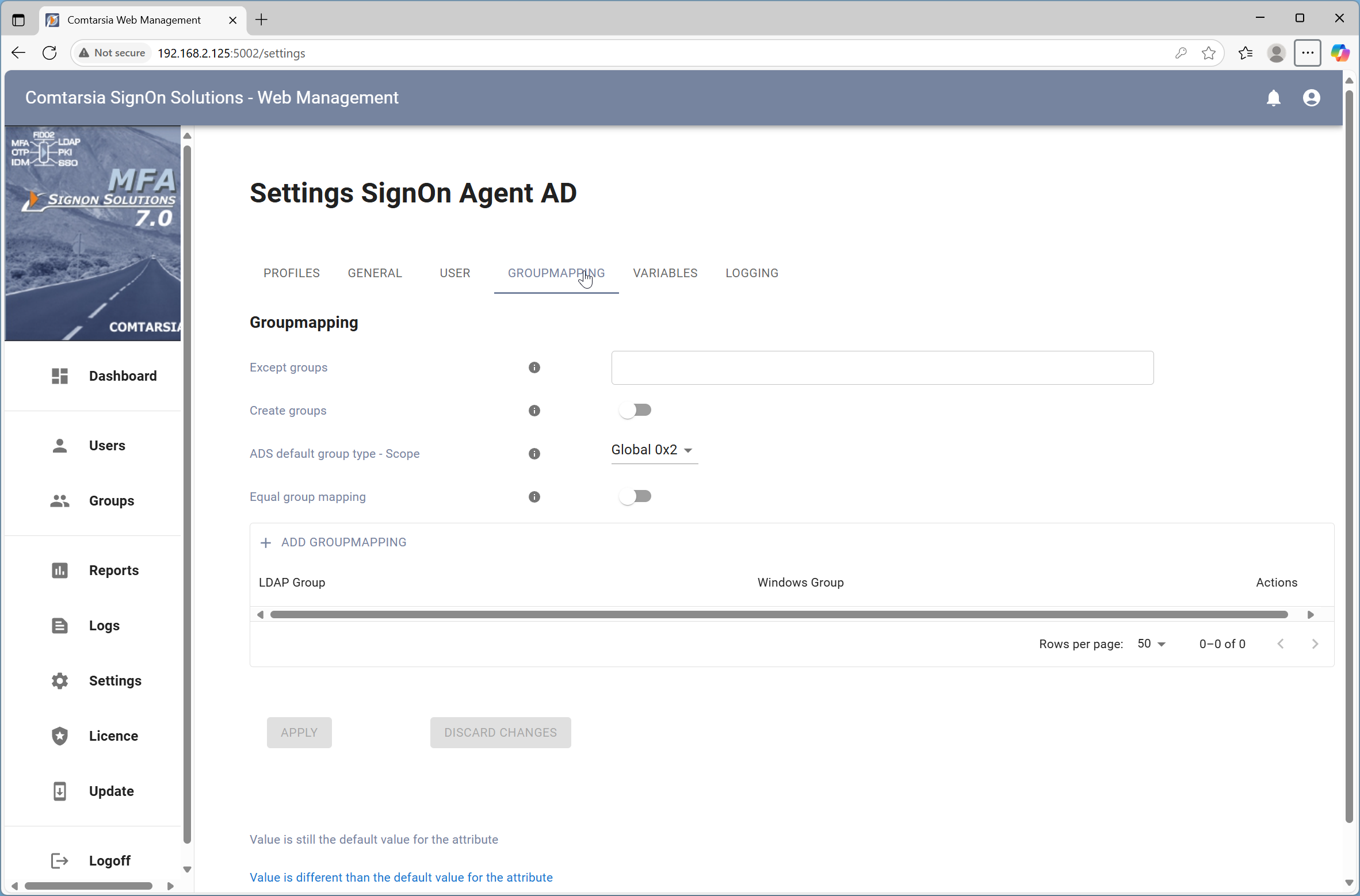
The group-mapping functions allows assign active directory group membership depending of the LDAP group membership of LDAP user. The LDAP group list are sent to the SignOn Agent via the the internal variable GROUP. By using the variable manger information of ldap attributes or from another sources can be added to this list by using the variable manager.
The parameter Except groups defines a comma separated list of group names for which no operation should be carried out. (The user won't be added to, nor removed from these groups.)
The parameter ADS default grouptype defines whether Domain local, Global or Universal groups should be used.
If Equal group-mapping is enabled, the group names won't be altered by the mapping list. Each LDAP Group will be mapped to a system group one-to-one. Otherwise, a manual “group mapping” list can be specified.
(also see: LDAP-groups and AttributeBasedGroups on the SignOn Proxy configuration)
7. Variables
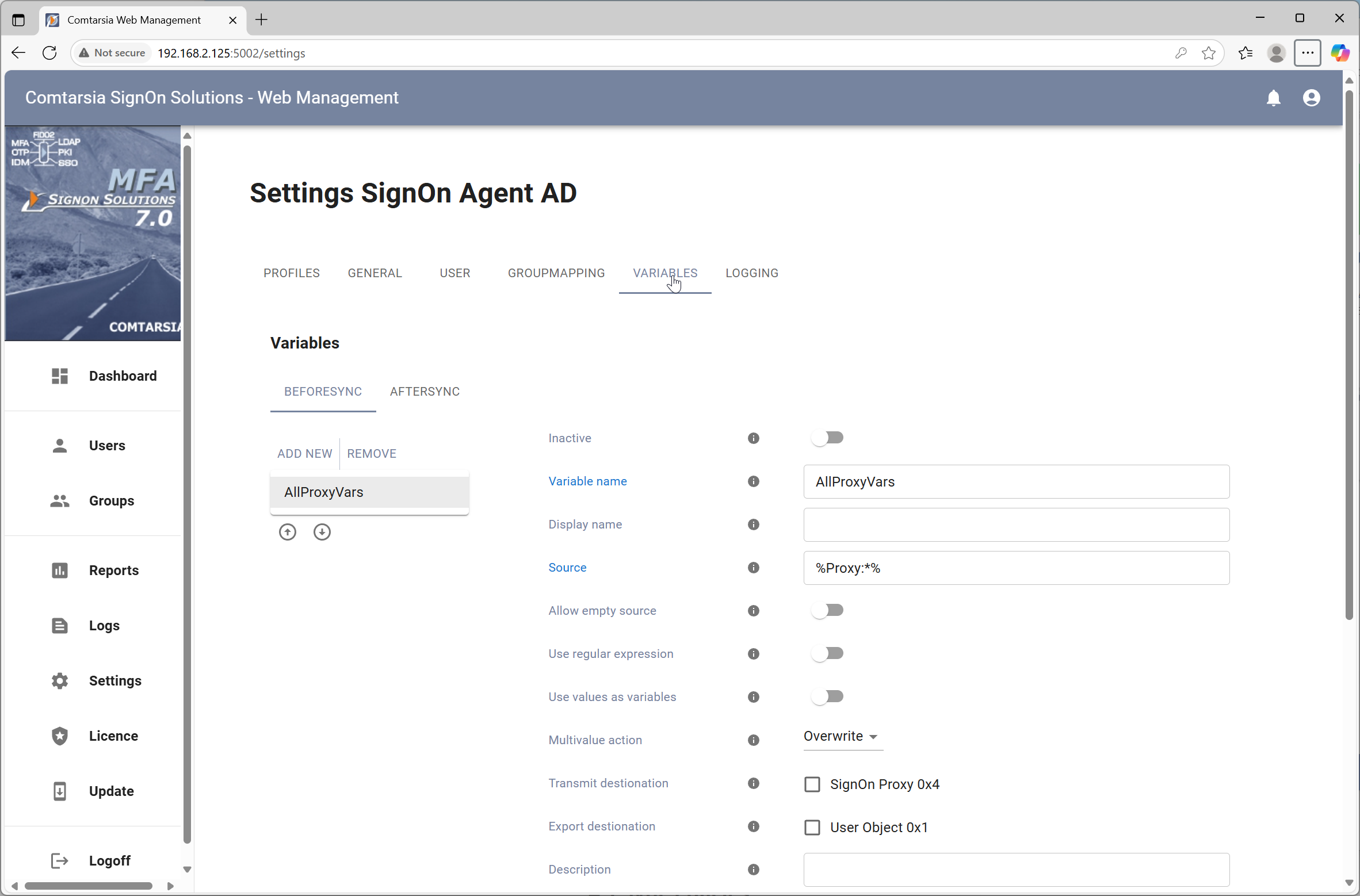
Variables are placeholders for variable values which can be obtained from different sources and processed and exchanged between the products within the Comtarsia product family. The values can also be exportet to the respective target systems.
Examples for possible sources: LDAP user object; Windows registry, Computer environment variables, internally provided values. Examples for possibe export targets: Attributes of the Windows user object (ie. comment, home/profile path, full name); user environment.
The variables can be used/modified at two different points in time which are defined by the tabs "Before Sync" and "After Sync".
- Before Sync: Variables will be accessed before the user synchronisation (thus they can also be sent to the SignOn Proxy/SignOn Agent)
- After Sync: Variables will be processed after the user synchronisation Thus values can be sent back by the SignOn Agent/SignOn Proxy and processed.
The variables will also be processed in order (from top to bottom). The up/down arrow buttons can be used to change that order.
The Variable name specifies the name of the variable. If the value has to be exportet, the name has to match with the name of the target variable and/or the name of the target attribute.
The Display name specifies the name to be displayed in the variables list (at the left side). This parameter is used by the configuration utility only and is meant to help organising the variables.
Via "Export Variable to", variables can be exportet to different target systems.
- User object: The value of the user obect (with the name of the value) will be set to the value of the variable.
- User environment: The variable will be exported into the user environment (Windows environment variable).
With Hold variables can be disabled temporarly.
Value
The Source defines the source/data of the variable. This field can contain text as well as other variables (between two '%'). To use '%' as part of the value '%%' has to be used and will be replaced by '%' rather than used as a variable. The "+" button offers a dialog to add easy-to-use variable source templates.
The MultiValue action defines how to handle multi value variables (variables which represent an array).
- Overwrite: A possibly existing value will be overwritten.
- Delete: The variable will be deleted.
- DeleteValue: The resulting value will be removed from the existing variable (array).
- AddValue: The resulting value will be added to the variable (array). (ie. to add a group to the existing list of groups)
Use regular expression enabled the 'regular expressions' functionality for this variable..
Expression defines the regular expression which has to be applied to the resolved value (content/data) of the source. If the source also contains variables, these will be replaced before the regular expression is applied.
The Formatter defines how to build the resulting value by applying the regular expression on the source value.
The Index can be used to refer to a specific match if a necessarily more ambiguous regular expression results in more than one match. Usually the index is 0 unless it's impossible to make the regular expression specific enough to result in only 1 match.
The Flags is a bitmask which specifies the operation mode of the regular expression.
Valid Flags:
match_default 0,
match_not_bol 0x00000001, /* first is not start of line */
match_not_eol 0x00000002, /* last is not end of line */
match_not_bob 0x00000004, /* first is not start of buffer */
match_not_eob 0x00000008, /* last is not end of buffer */
match_not_bow 0x00000010, /* first is not start of word */
match_not_eow 0x00000020, /* last is not end of word */
match_not_dot_newline 0x00000040, /* \n is not matched by '.' */
match_not_dot_null 0x00000080, /* '\0' is not matched by '.' */
match_prev_avail 0x00000100, /* *--first is a valid expression */
match_init 0x00000200, /* internal use */
match_any 0x00000400, /* don't care what we match */
match_not_null 0x00000800, /* string can't be null */
match_continuous 0x00001000, /* each grep match must continue */
/* uninterupted from the previous one */
match_partial 0x00002000, /* find partial matches */
match_stop 0x00004000, /* stop after first match (grep) V3 only */
match_not_initial_null 0x00004000, /* don't match initial null, V4 only */
match_all 0x00008000, /* must find the whole of input even if match_any is set */
match_perl 0x00010000, /* Use perl matching rules */
match_posix 0x00020000, /* Use POSIX matching rules */
match_nosubs 0x00040000, /* don't trap marked subs */
match_extra 0x00080000, /* include full capture information for repeated captures */
match_single_line 0x00100000, /* treat text as single line and ignor any \n's when matching ^ and $. */
match_unused1 0x00200000, /* unused */
match_unused2 0x00400000, /* unused */
match_unused3 0x00800000, /* unused */
match_max 0x00800000,
format_perl 0, /* perl style replacement */
format_default 0, /* ditto. */
format_sed 0x01000000, /* sed style replacement. */
format_all 0x02000000, /* enable all extentions to sytax. */
format_no_copy 0x04000000, /* don't copy non-matching segments. */
format_first_only 0x08000000, /* Only replace first occurance. */
format_is_if 0x10000000, /* internal use only. */
format_literal 0x20000000, /* treat string as a literal */
Transmit Destination
The Transmit Destination specifies to which other Comtarsia SignOn products this variable should be sent to. (Invalid destinations are greyed out)
If the Transmit Destination 'SignOn Agent 0x8' is set (only possible on the SignbOn Proxy) the option Domains can be used to specify to which SignOn Agent domains this variable should be sent. If this field is empty, the variable will be sent to all SignOn Agents.
8. Logging
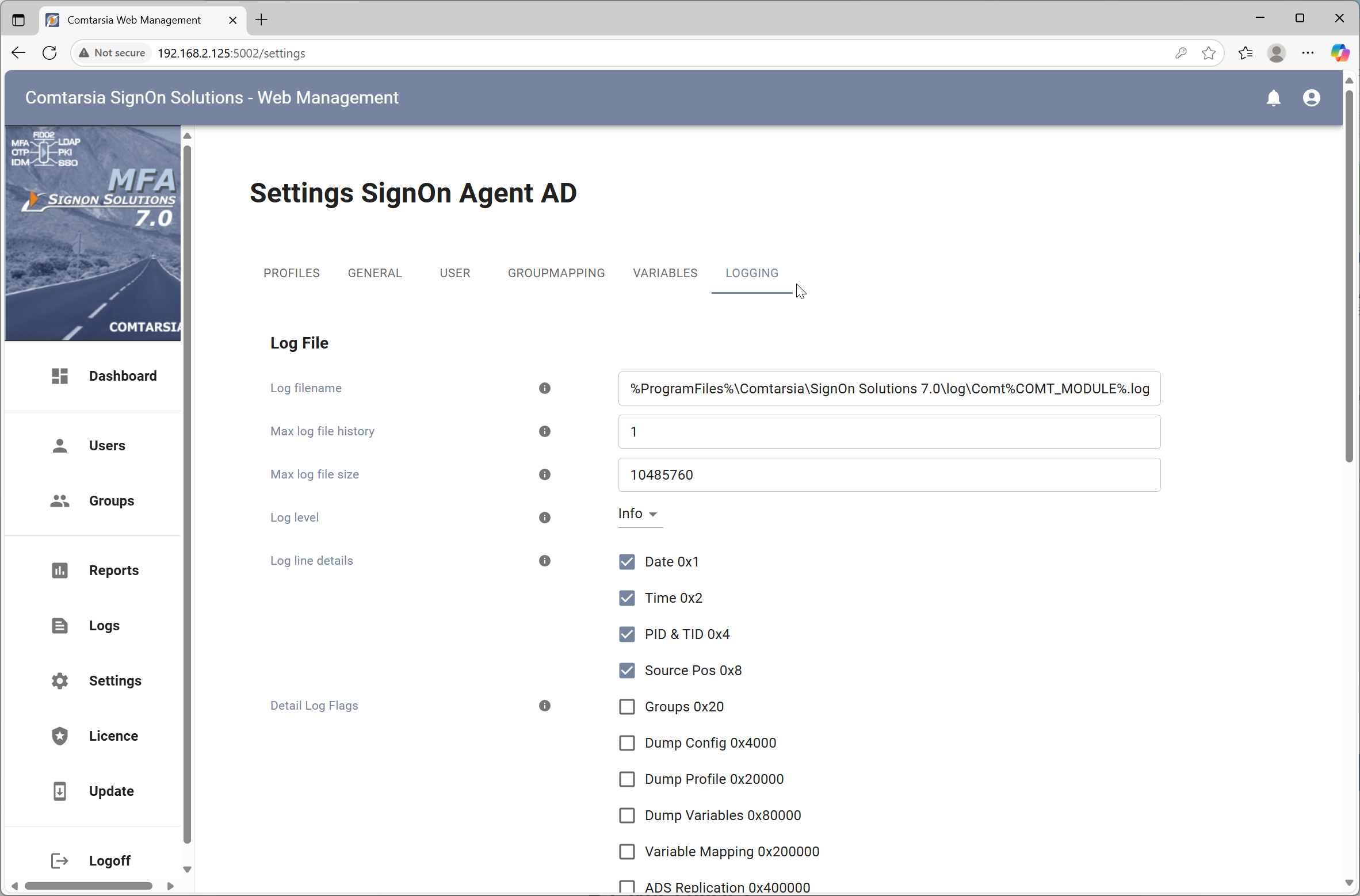
8.1 Log File
Enable Enables/disables writing to the log file.
Loglevel The LogLevel defines the verbosity of the log written to the specified file. The “detail log flags” are handled independently of the LogLevel. Eg: It’s perfectly valid to use “LogLevel”=None, and “Detail Log Flags”=Monitor to only log “monitoring”-messages.
- None: No logging, except detail log flags.
- Error: Only errors and specified detail log flags.
- Exception: As Error, and exception messages.
- Warn: As Exception, and warnings.
- Info: As Warn, and additional information
- Detail MSG: Everything (except unspecified log flags which have to be enabled separately)
Log filename Defines the path to the log file.
Max logfile size Defines the size at which the logfile should be rotated.
Max logfile history Defines the amount of logfiles to be rotated.
Detail Log Flags Detail Log Flags enable specific log output independent of the Loglevel. The Detail Log Flag "Monitor" is recommended for centralized monitoring.
Log Line Details Defines which details are to be included in each log line.
- Date
- Time
- PID & TID: Process and thread ID.
- Source pos: The position (line) in the source code.
[Image placeholder: image012.gif]
8.2 SysLog
Enable Enables/disables forward of log messages to a syslog server.
Loglevel The LogLevel defines the verbosity of the log written to the specified file. The “detail log flags” are handled independently of the LogLevel. E.g.: It’s perfectly valid to use “LogLevel”=None, and “Detail Log Flags”=Monitor to only log “monitoring”-messages.
- None: No logging, except detail log flags.
- Error: Only errors and specified detail log flags.
- Exception: As Error, and exception messages.
- Warn: As Exception, and warnings.
- Info: As Warn, and additional information
- Detail MSG: Everything (except unspecified log flags which have to be enabled separately)
Syslog host Defines the central SysLog host to which the SysLog messages will be sent.
Syslog facility Specifies the SysLog facility of the log messages.
Detail Log Flags Detail Log Flags enable specific log output independent of the Loglevel. The Detail Log Flag "Monitor" is recommended for centralized monitoring.
Log Line Details Defines which details are to be included in each log line.
- Date
- Time
- PID & TID: Process and thread ID.
- Source pos: The position (line) in the source code.
